Carbon Monoxide: one of the most important air pollutants

SRON’s role in carbon monoxide research
In 2017 the European Space Agency (ESA) successfully launched the Sentinel-5 Precursor satellite, carrying the instrument Tropospheric Monitoring Instrument (TROPOMI) as its only payload. TROPOMI is developed by a Dutch consortium including SRON. One of its primary products is the measurement of atmospheric carbon monoxide (CO) using SRON’s operational software. It offers daily global coverage with a spatial resolution of 7×5.5 km2. SRON will also be involved in the operational processing of CO data from the upcoming Sentinel-5 mission.
In the decade before, from 2003 to 2012, it was the SCIAMACHY instrument that first measured atmospheric CO concentrations. SCIAMACHY was developed by a German/Dutch/Belgian consortium including SRON, and was one of ten instruments onboard ESA’s Environmental Satellite (ENVISAT). With a 2.3 mu spectral range it was sensitive to CO in the atmosphere near the Earth’s surface.
Recent CO Pollution news
News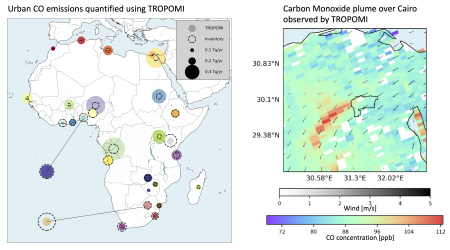
Satellite observations African cities: carbon monoxide emissions deviate from inventories
Interactive Fire Data Map
Fire DataCarbon Monoxide Publications
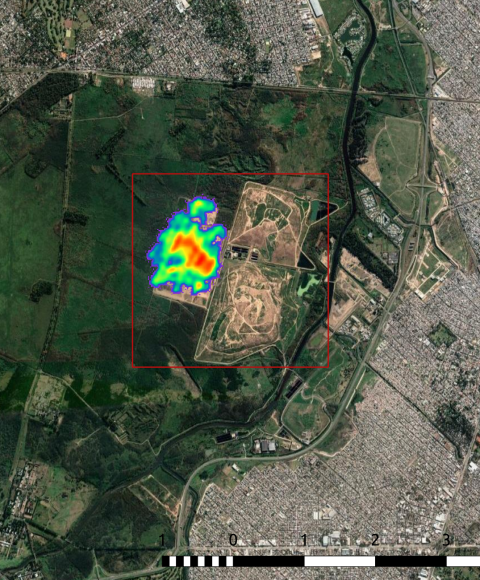
Plume detection and emission estimate for biomass burning plumes from TROPOMI carbon monoxide observations using APE v1.1
This paper presents the automated plume detection and emission estimation algorithm (APE), developed to detect CO plumes from isolated biomass burning events and to quantify the corresponding CO emission rate. APE uses the CO product of the Tropospheric Monitoring Instrument (TROPOMI) on board the Copernicus Sentinel-5 Precursor (S5P) satellite, launched in 2017, and collocated active fire data from the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS), the latter flying 3 min ahead of S5P. After identifying appropriate fire events using VIIRS data, an automated plume detection algorithm based on traditional image processing algorithms selects plumes for further data interpretation. The approach is based on thresholds optimized for data over the United States in September 2020. Subsequently, the CO emission rate is estimated using the cross-sectional flux method, which requires horizontal wind fields at the plume height. Three different plume heights were considered, and the ECMWF Reanalysis v5 (ERA5) data were used to compute emissions. A varying plume height in the downwind direction based on three-dimensional Lagrangian simulation was considered appropriate. APE is verified for observations over Australia and Siberia. For all fire sources identified by VIIRS, only 16 % of the data corresponded to clear-sky TROPOMI CO data with plume signature. Furthermore, the quality filters of APE resulted in emission estimations for 26 % of the TROPOMI CO data with plume signatures. Visual filtering of the APE’s output showed a true-positive confidence level of 97.7 %. Finally, we provide an estimate of the emission uncertainties. The greatest contribution of error comes from the uncertainty in Global Fire Assimilation System (GFAS) injection height that leads to emission errors <100 %, followed by systematic errors in the ERA5 wind data. The assumption of constant emission during plume formation and spatial under-sampling of CO column concentration by TROPOMI yields an error of <20 %. The randomized errors from the ensemble ERA5 wind data are found to be less than 20 % for 97 % of the cases.
Sixteen years of MOPITT satellite data strongly constrain Amazon CO fire emissions
Despite the consensus on the overall downward trend in Amazon forest loss in the previous decade, estimates of yearly carbon emissions from deforestation still vary widely. Estimated carbon emissions are currently often based on data from local logging activity reports, changes in remotely sensed biomass, and remote detection of fire hotspots and burned area. Here, we use 16 years of satellite-derived carbon monoxide (CO) columns to constrain fire CO emissions from the Amazon Basin between 2003 and 2018. Through data assimilation, we produce 3 d average maps of fire CO emissions over the Amazon, which we verified to be consistent with a long-term monitoring programme of aircraft CO profiles over five sites in the Amazon. Our new product independently confirms a long-term decrease of 54 % in deforestation-related CO emissions over the study period. Interannual variability is large, with known anomalously dry years showing a more than 4-fold increase in basin-wide fire emissions relative to wet years. At the level of individual Brazilian states, we find that both soil moisture anomalies and human ignitions determine fire activity, suggesting that future carbon release from fires depends on drought intensity as much as on continued forest protection. Our study shows that the atmospheric composition perspective on deforestation is a valuable additional monitoring instrument that complements existing bottom-up and remote sensing methods for land-use change. Extension of such a perspective to an operational framework is timely considering the observed increased fire intensity in the Amazon Basin between 2019 and 2021.
Air quality impacts of COVID-19 lockdown measures detected from space using high spatial resolution observations of multiple trace gases from Sentinel-5P/TROPOMI
The aim of this paper is to highlight how TROPOspheric Monitoring Instrument (TROPOMI) trace gas data can best be used and interpreted to understand event-based impacts on air quality from regional to city scales around the globe. For this study, we present the observed changes in the atmospheric column amounts of five trace gases (NO2, SO2, CO, HCHO, and CHOCHO) detected by the Sentinel-5P TROPOMI instrument and driven by reductions in anthropogenic emissions due to COVID-19 lockdown measures in 2020. We report clear COVID-19-related decreases in TROPOMI NO2 column amounts on all continents. For megacities, reductions in column amounts of tropospheric NO2 range between 14 % and 63 %. For China and India, supported by NO2 observations, where the primary source of anthropogenic SO2 is coal-fired power generation, we were able to detect sector-specific emission changes using the SO2 data. For HCHO and CHOCHO, we consistently observe anthropogenic changes in 2-week-averaged column amounts over China and India during the early phases of the lockdown periods. That these variations over such a short timescale are detectable from space is due to the high resolution and improved sensitivity of the TROPOMI instrument. For CO, we observe a small reduction over China, which is in concert with the other trace gas reductions observed during lockdown; however, large interannual differences prevent firm conclusions from being drawn. The joint analysis of COVID-19-lockdown-driven reductions in satellite-observed trace gas column amounts using the latest operational and scientific retrieval techniques for five species concomitantly is unprecedented. However, the meteorologically and seasonally driven variability of the five trace gases does not allow for drawing fully quantitative conclusions on the reduction in anthropogenic emissions based on TROPOMI observations alone. We anticipate that in future the combined use of inverse modeling techniques with the high spatial resolution data from S5P/TROPOMI for all observed trace gases presented here will yield a significantly improved sector-specific, space-based analysis of the impact of COVID-19 lockdown measures as compared to other existing satellite observations. Such analyses will further enhance the scientific impact and societal relevance of the TROPOMI mission.
Meet our partners
We collaborate with climate researchers and modelers, and together contribute to the development of physical instruments and the promotion of scientific activities outside SRON.
-

ESA
-
ISISspace
-

KNMI
-

TNO
-

VU
-

WUR
Our other research themes
-
Methane
-
Responsible for ¼ of human-made greenhouse effect
-
About 30 times more powerful than CO₂ (GWP-100)
-
Large emissions from fossil fuel industry, landfills, livestock
-
-
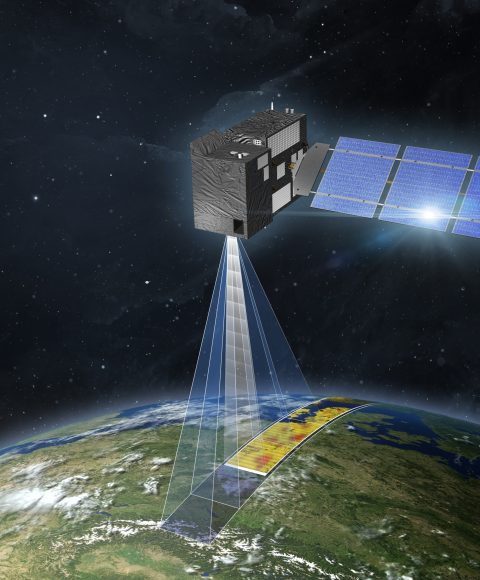

CO₂
-
Most important human-made greenhouse gas
-
Hard to monitor emissions because of long lifetime
-
-
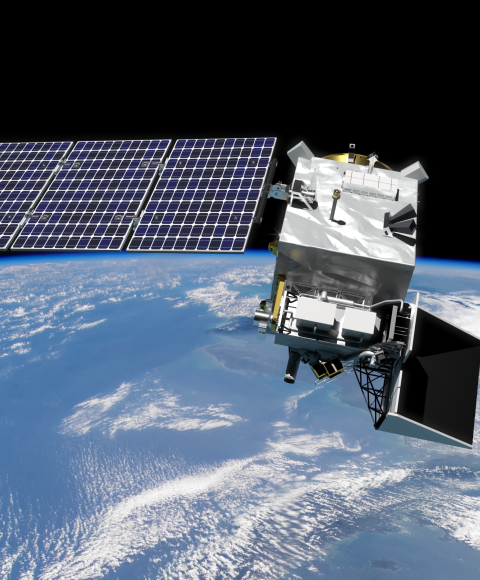

Aerosols and Clouds
-
Small particles in the atmosphere
-
Largest unknown factor in climate change
-
Strong impact on air quality
-